What Your Baby’s Fetal Position Could Mean for Their Birth
As you draw near the end of the third trimester, your baby’s position will begin to take root—and possibly reshape your delivery plans.
Over the past few months, you’ve felt your acrobatic bundle twist, flip, and tumble inside you, but around 32-36 weeks of pregnancy, your babe will settle into a position to get ready for their grand entrance. Usually, babies will be head down—but not always! Knowing your baby’s position will help you be better prepared for labor day possibilities. Here are the phrases that your doctor might use to describe fetal presentation in the womb.
Vertex (or Cephalic) Presentation
Baby’s head is going to be pushed out first, but there are more specific terms depending on which way they’re facing. The vertex presentations are further classified according to the position of the occiput (the back of baby’s head or skull), including right, left, transverse, anterior, or posterior.
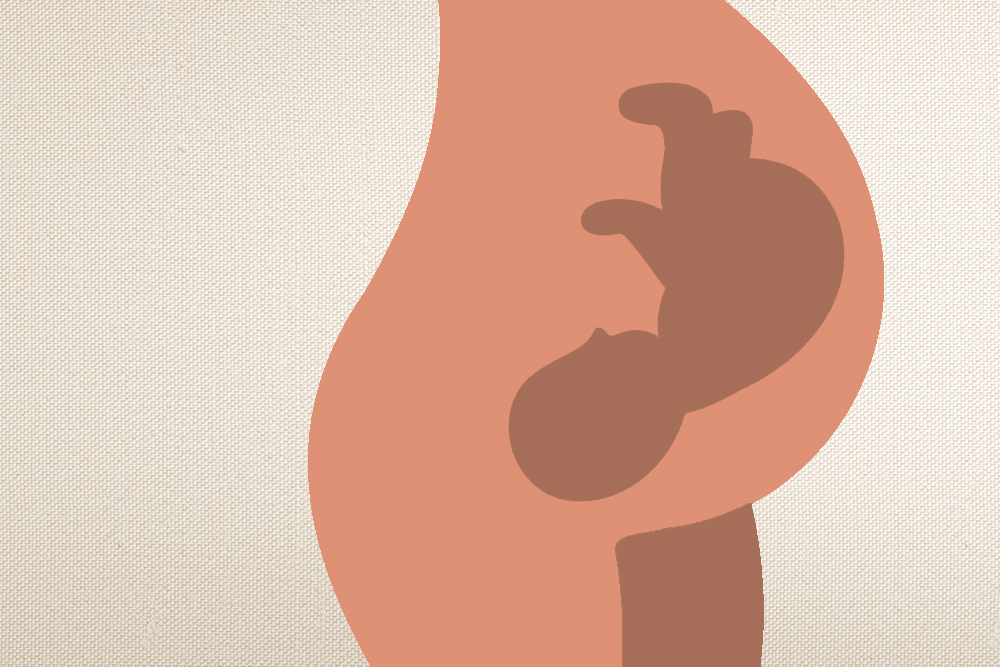
Occiput Anterior (AKA Facing Downward)
Baby is headfirst and the back of the head is against your belly. Usually, the head will be turned slightly, so your medical care provider might add a “left” or “right” to the phrase: left occiput-anterior position (LOA); right occiput-anterior position (ROA). This is the most common and preferred position for a vaginal birth.
Occiput Posterior (AKA Facing Upward)
Baby is headfirst and the back of their head is closest to your back. This is another instance where your doctor can specify “left” or “right” in describing whether baby’s face is turned: left occiput-posterior position (LOP); right occiput-posterior position (ROP).
Occiput Transverse (AKA Facing Sideways)
Baby is headfirst and facing toward either side of the birthing parent’s side, halfway between a posterior and anterior position. If facing the left thigh, baby is said to be in the right occiput-transverse position (ROT); when facing the right thigh, baby is in the left occiput-transverse position (LOT).
Breech
Your babe’s head is near the top of the uterus, their rear end is facing the birth canal, and their tiny toes are pointing skyward. A breech baby will often change position and turn head-down by 36 weeks. It’s possible to birth vaginally, but a cesarean section (C-section) is usually recommended.
Complete Breech Presentation
This presentation is the same as standard breech, except baby’s legs will be bent at the knees with their feet tucked down near their bottom.
Frank Breech
Baby’s legs are folded flat against their head, and their rear is closest to the birth canal. This is the most common type of breech position.
Transverse Lie
What it means: Your wee one is lying sideways, horizontally across your uterus. Their back or their hands and feet will be nearest to the birth canal, depending on which way they’re facing. While this position is uncommon, a baby in the transverse lie position will not fit into the vaginal canal, making a safe vaginal delivery unlikely, if not impossible. Your OB-GYN will likely recommend a C-section.
Thankfully, most babies will turn themselves into the correct position for labor. If not, your doctor might suggest an external cephalic version to help manually rotate the baby from the outside using strategic pressure on the baby’s head and bottom. It sounds scary, but complications are rare. A C-section may be needed if your bambino is still transverse as their delivery day approaches.







